A review of dozens of studies shows that Omega-3 fatty acids have a positive effect on the length of telomeres, reported to be a marker of biological aging.
Research on telomeres has exploded in recent years as scientists have demonstrated how telomere length can be used to predict life expectancy.
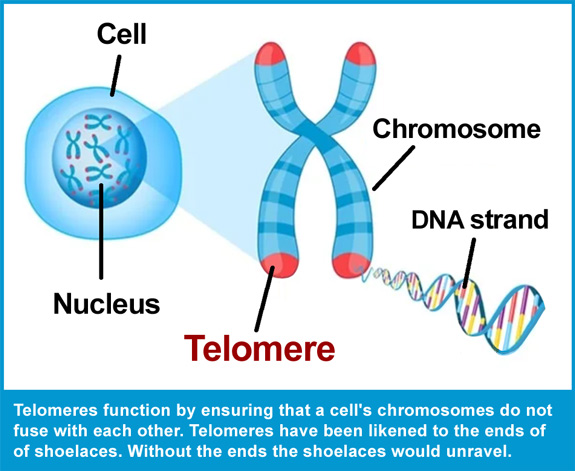
Telomeres are part of cells. They are DNA sequences that are found at the end of chromosomes, and they shorten as cells replicate and age.
The length of these telomeres do not always correlate with chronological age. Instead the length is dictated by a person’s overall health. The longer the telomeres, the longer the life expectancy.
Not surprisingly, scientists are very interested in nutrients and lifestyle factors that can keep telomeres long—and the new research appears to show that Omega-3 fatty acids do just that.
It’s all about inflammation
The biological mechanism that makes Omega-3s beneficial in this way lies in its ability to reduce inflammation.
Inflammation is caused by oxidative stress and is strongly associated with accelerated telomere shortening and dysfunction. One of the many health benefits of Omega-3 fatty acids is its function as an antioxidant, making it a potent natural anti-inflammatory.
Theoretically any and all antioxidants should be telomere-shortening superheroes; however, with the thousands of antioxidants available in nature, it will take a very long time to prove the theory universally.
Notwithstanding this daunting task, some antioxidant nutrients, such as selenium, have already been studied and proven effective at promoting telomere health. (See our related post on selenium here.)
The new study on Omega-3s was conducted in Poland at the Institute of Genetics and Animal Biotechnology of the Polish Academy of Sciences.
Review includes three categories of research
The researchers’ review of the existing scientific literature included seven observational (non-interventional) studies, which indicated that, in general, Omega-3 fatty acids played a positive role in telomere biology.
These results, however, merely show correlation and not causation, which led the researchers to move on to reviewing randomized dietary studies that used Omega-3 supplements. The researchers found four such intervention studies.
The randomized studies were performed on a range of populations, including mothers and their infants; people with chronic renal impairment; elderly people suffering from mild cognitive impairment; and, finally, healthy, overweight, middle-aged and elderly people.
The doses used in these studies ranged from just over one gram per day to four grams per day of Omega-3 fatty acids.
Finally, the third category the researchers reviewed was animal studies. Though animal studies cannot always be compared directly to human studies, it is easier to conduct research on animals—meaning a greater volume of data is available to share and analyze.
The overwhelming results—culled from all three categories—showed a clear benefit of Omega-3 supplementation in helping maintain the length of telomeres.
All of the observational studies demonstrated a positive link; as did all of the animal studies. Only the randomized studies had somewhat mixed results, though, even in this category, most of the studies found positive results for Omega-3 supplements.
“The ability of Omega-3 fatty acids to reduce these negative effects is related not only to their well-documented beneficial effect on a number of ‘lifestyle’ diseases, but also to their beneficial effects on telomere biology,” the scientists wrote in the study summary.
“The use of Omega-3 fatty acids to reduce accelerated telomere attrition and, consequently, counteract premature aging and reduce the risk of age-related diseases raises high hopes.”
Lifestyle factors speed up telomere shortening
In addition to commenting on the positive benefit of Omega-3 supplementing, the researchers noted lifestyle factors that also contribute to oxidative stress and telomere shortening.
The list included: chronic stress, smoking, obesity, alcohol consumption and depression.
Whether or not prescription drugs also contribute to telomere shortening was not mentioned.
The study was published in Nutrients in September 2022.
All three Omega-3 essential fatty acids can be found in Optimal E.F.A. by Optimal Health Systems:
• A-linolenic acid (ALA)
• Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
• Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
Click the banner ad on this page, or visit the product info page here.
– – –
Sources: Nutrients/MDPI database.