Modern society is inarguably toxic. Each day we are exposed to thousands of toxic substances, many of which wreak havoc in our bodies.
Of these substances phthalates are probably the most ubiquitous.
Phthalates are substances added to plastics to increase their flexibility and durability—sometimes referred to as a “plasticizers”.
While not all plasticizers are phthalates, phthalates are the most common. And that’s what makes them so dangerous… because they are everywhere.
High priority pollutant
Wikipedia states: “Due to the ubiquity of plasticized plastics, the majority of people are exposed to some level of phthalates. For example, most Americans tested by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have metabolites of multiple phthalates in their urine.”
Another source, a 2024 study by Consumer Reports, found phthalates in all but one of the 85 brand-name grocery store and fast food items they tested.
Phthalates are unique in the danger they present to humans because they are hormone disruptors (aka endocrine disruptors). This refers to their inherent ability to mimic natural hormones and act as endocrine disruptors upon entering the body.
Because of this clear and present danger they present phthalates are referred to as a “high-priority pollutant”.
The Center for Science in the Public Interest describes it this way: “Studies indicate that some phthalates are hormone disruptors. ‘Disrupt’ means that a chemical can turn on, turn off, or change the signals sent by hormones like estrogens, testosterone, thyroid hormones, and insulin. Accordingly, phthalates are linked to health harms including reproductive issues, miscarriage, breast cancer, and diabetes.”
In addition, Wikipedia notes that hormone disruption also retards child development and growth early in life; contributes to the obesity epidemic; affects cardiovascular health; and is implicated in the neurological issues that plague modern society.
Fortunately there is some good news: For a number of years scientists have been reseaching enzymes that can destroy, or at least degrade, toxins like phthalates.
In 2014 a ground-breaking study identified a new enzyme derived from the Sulfobacillus acidophilus microbe strain that had the potential to take “phthalate-destruction” to the next level.
According to Chinese researchers, the newly-identified nutrient is able to “enzymatically degrade” phthalate esters (PAEs).
“To our knowledge, this enzyme is a new esterase identified from thermophiles that is able to degrade various PAEs at high temperatures,” the researchers wrote in the study findings, published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
And now that enzyme—originally designated as “EstS1”—is available as Phthalazyme. The name “Phthalazyme” was chosen in recognition of the enzyme’s unique ability to break-down phthalates.
In the original study that identified EstS1 (Phthalazyme), researchers cloned 15 different esterase genes from bacteria and tested their effectiveness is breaking-down toxins.
Among the different esterases compared, the new EstS1, which was cloned from Sulfobacillus acidophilus, showed the most promise. The scientists then proceeded with expanded testing.
Potent AND stable
While this testing is technical and extensive (a PDF of the full study can be downloaded here), it should be noted that the EstS1 was tested against a number of common toxins.
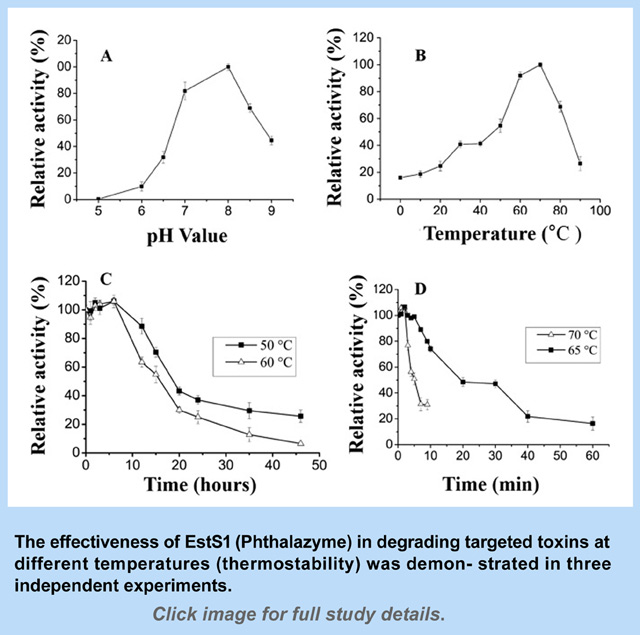
It was also tested at varying temperatures. This is an important consideration since targeted locations for degrading toxins—such as in the human gut—would not always be at a optimum temperature. (See sidebar graphs for more info.)
“The potential value of EstS1 was demonstrated by its ability to effectively hydrolyze 35% to 82% of PAEs within two minutes at 37°C, with all substrates being completely degraded within 24 hours. At 60°C, the time required for complete hydrolysis of most PAEs was reduced by half,” the researchers noted in the study findings.
“Our results demonstrate that this esterase, with its good thermal stability, is a valuable biocatalyst for general degradation of various PAEs widely distributed in the environment. It is able to degrade PAEs over long durations under ordinary temperatures and is particularly useful for the degradation of PAEs at relatively high temperatures.”
As a supplement industry leader Optimal Health Systems is proud to be the first to offer Phthalazyme in its new cutting edge product, Optimal Chemzyme.
Optimal Chemzyme is a unique formula developed to address the alarming increase in food additives and harmful chemicals found in the modern diet. Phthalazyme is a critical part of this formula since it is the first and only enzyme specifically designed to digest and detoxify phthalates.
– – –
Sources: Applied and Environmental Microbiology (PubMed), Wikipedia (phthalates).