A new in vitro study that appears in the scientific journal Redox Biology has provided the first evidence that nitric oxide inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2.
SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Scientists at the Zoonosis Science Center at Uppsala University in Sweden conducted the research.
“To our knowledge, nitric oxide is the only substance shown so far to have a direct effect on SARS-CoV-2,” says Åke Lundkvist, a professor at Uppsala University, who led the study and was the senior author of the report.
Since there is still no effective cure for COVID-19, the main emphasis in the treatments tested has been on relieving symptoms. This can shorten hospital stays and reduce mortality.
Up until now, though, it has not been possible to prove if any of these treatments are able to retard the actual virus behind the infection.
“Our hope is that inhalation of nitric oxide might be an effective form of treatment,” said Dr. Lundkvist. “The dosage and timing of starting treatment probably play an important part in the outcome, and now need to be explored as soon as possible.”
Supplement now or hospital treatment later?
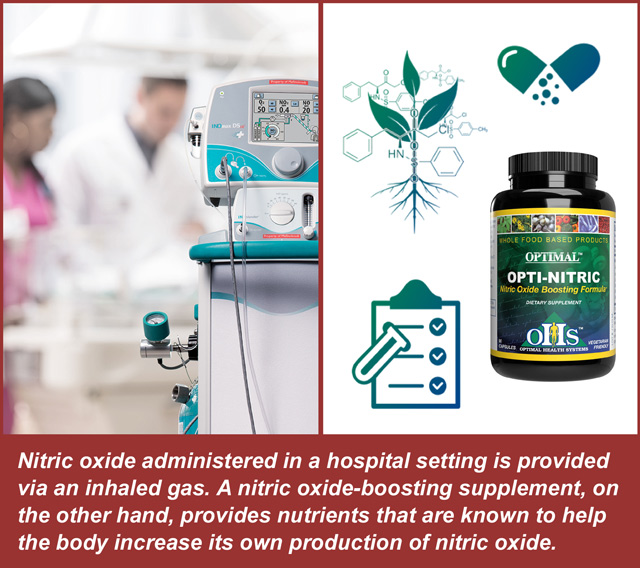
The higher dose of nitric oxide provided in a medical setting via inhalation also gives some insight to the possible benefit provided by nitric oxide-building nutritional supplements.
Supplements that help improve nitric oxide levels in the body are growing in popularity, and the new study helps reinforce the assertion that boosted levels of nitric oxide equates to an improved immune system.
This has already shown to be the case with vitamins A, C and D and the mineral zinc. With all of these nutrients, regular supplementing has been shown to negate the need for high dose “emergency” administration at the hospital.
A study launched in October 2020 by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will will test if this kind of oral supplementing also works with regards to nitric oxide.
For this survey, the FDA approved an outpatient study testing the safety and efficacy of an oral supplement in treating African Americans diagnosed with COVID-19.
Unfortunately, results from that study are not expected to be published until June 2021.
What is nitric oxide?
Nitric oxide is a compound produced naturally in the body.
In mammals, including humans, it acts as a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes.
It also functions like a hormone in controlling various organs. It regulates, for example, tension in the blood vessels and blood flow between and within organs.
In acute lung failure, nitric oxide can be administered as inhaled gas—in low concentrations—to boost the blood-oxygen saturation level. Research shows that this results in reduced lung inflammation.
In this way nitric oxide offers protection against infections—as both an antibacterial and antiviral.
Previous research
The study of nitric oxide as a treatment for respiratory ailments is not new; however, even positive results have a tough time making inroads against established medical protocols. Oftentimes it takes the threat of a pandemic to get the ball rolling.
A small clinical study conducted in Beijing in 2004 found that inhaled nitric oxide at low concentrations not only works as a vasodilator for SARS patients (improving oxygenation of their blood) but also as an antiviral agent.
According to Medical News Today, previous studies show that nitric oxide is effective against the herpes virus, coxsackievirus, and hantavirus.
Since nitric oxide is produced in the body, many ingredients have been studied to ascertain their “nitric oxide-boosting” ability.
Opti-Nitric by Optimal Health Systems contains a blend of these nutrients: L-arginine, L-citrulline, Beta-alanine and OKG (Ornithine alpha-ketoglutarate).
Learn more at the Opti-Nitric product info page here.
– – –
Sources: Redox Biology / ScienceDirect, Science Daily, Medical News Today.